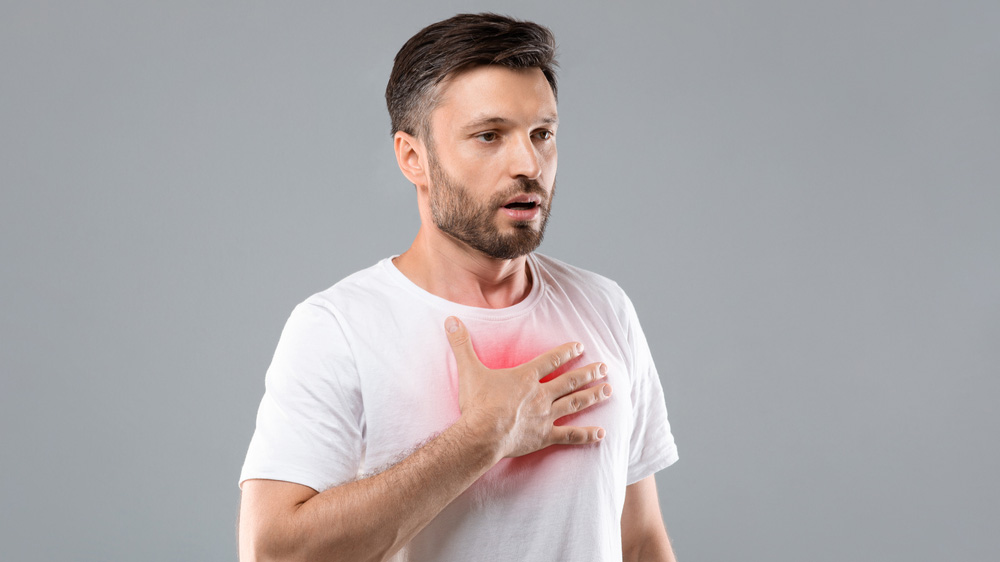
In a world where stress is omnipresent and emotions constantly fluctuate, understanding their impact on our physical health is essential. Emotions are not merely abstract feelings; they have a real and measurable influence on our bodies. Anger, fear, joy, sadness, or love: each emotion modifies our physiological functions, sometimes for the better, sometimes for the worse. But how do these inner states regulate our bodily well-being? Let’s dive into the fascinating connection between mind and body and learn how emotions influence physical health.
The Link Between Emotions and the Nervous System
Emotions influence physical health in a variety of ways, the first one being because of their deep link to our nervous system. The limbic brain, particularly the amygdala and hippocampus, manages our emotional reactions and activates various physiological responses. In the case of intense fear, for example, the amygdala stimulates the sympathetic nervous system, releasing cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones prepare the body for a fight-or-flight reaction, increasing heart rate and blood pressure.
On the other hand, positive emotions activate the parasympathetic nervous system, which promotes relaxation, reduces oxidative stress, and improves cell regeneration. Feelings of happiness or love stimulate the production of oxytocin, fostering an overall sense of well-being.
Stress and Inflammation: Dangerous Connections
Chronic stress, combined with persistent negative emotions (anxiety, anger, deep sadness), is a real-time bomb for the body. It promotes systemic inflammation, an aggravating factor for many chronic diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, and autoimmune disorders.
A study published in Psychosomatic Medicine shows that individuals suffering from prolonged emotional stress have higher levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines. These substances, when in excess, trigger inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and asthma.
Impact of Emotions on the Immune System
The immune system is another mechanism where we can see that emotions influence physical health directly. Chronic stress weakens immune defenses, making the body more vulnerable to infections. In contrast, laughter, gratitude, and personal satisfaction increase antibody production and stimulate natural killer (NK) cells, essential for fighting viruses and cancer cells.
A study from the University of California demonstrated that individuals practicing meditation and heart coherence show a significant reduction in stress hormones and improved immune resistance.
Influence of Emotions on the Cardiovascular System
Negative emotions have a significant impact on the heart and blood vessels. Chronic anxiety and depression are associated with an increased risk of coronary heart disease. Sudden outbursts of anger can cause a sharp rise in blood pressure, increasing the risk of strokes.
Conversely, positive emotions such as gratitude and joy release endorphins and dopamine, which regulate blood pressure and improve heart health.
Role of Emotions in Digestion and the Gut Microbiome
The digestive system is often referred to as the “second brain” due to the presence of a dense neural network and neurotransmitters influenced by our emotions. Stress and anxiety disrupt the gut-brain axis, leading to gastrointestinal disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), ulcers, and acid reflux.
Moreover, emotions directly influence the gut microbiome. A positive mindset and a healthy diet promote a balanced gut flora, which is essential for good digestion and a strong immune system.
How to Cultivate Emotions Beneficial for Health?
- Practice Gratitude: Keeping a gratitude journal improves mood and reduces inflammation.
- Meditation and Breathing: Heart coherence reduces cortisol and fosters a calm state.
- Regular Physical Exercise: Increases endorphins and reduces stress.
- Balanced Diet: Influences the microbiome and emotional balance.
- Positive Social Relationships: Strengthen oxytocin production, promoting well-being.
Conclusion
Emotions influence physical health in profound ways – they’re not just abstract psychological states but key drivers of immunity, heart function, digestion, and overall vitality. Learning to manage and direct them positively becomes a crucial strategy for maintaining overall balance.
Sources:
- Harvard Medical School – Emotions and physical health (link)
- American Psychological Association – The link between stress and inflammation (link)
- Mayo Clinic – Mind-body connection and wellness (link)
- National Institutes of Health – Impact of emotions on immune function (link)
- The Lancet Psychiatry – Mental health and physical diseases (link)