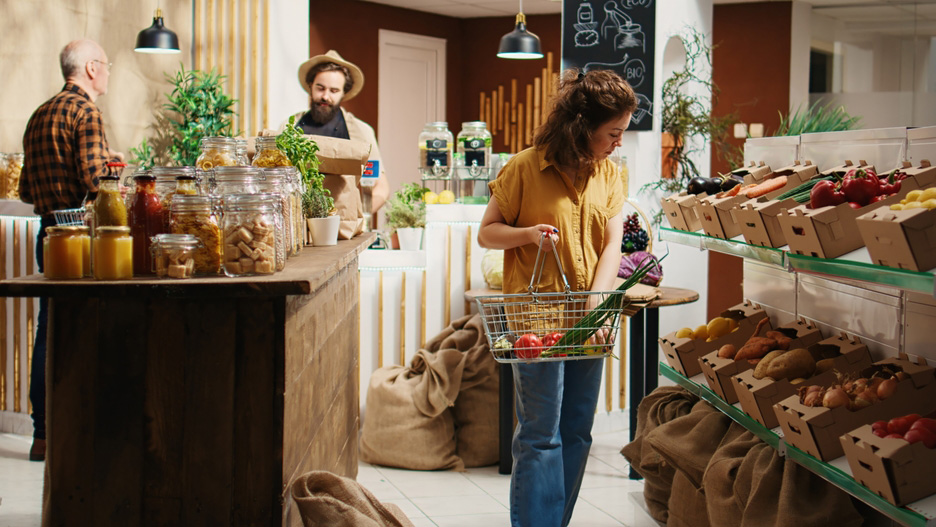
Ethical nutrition is more than a dietary choice; it’s a commitment to health and environmental sustainability. By embracing a lifestyle centered on ethical and nutritious food, we can nourish our bodies and nurture the planet. In this article, we’ll uncover how choosing foods that care for both our well-being and the Earth creates a harmonious balance between physical health and ethical living.
1- Ethical Nutrition: The Intersection of Health and Responsibility
Why Ethical Eating Matters
Every food choice impacts our health and shapes the planet’s future. Ethical nutrition focuses on consuming responsibly sourced foods that support physical well-being while minimizing ecological harm. From soil health to water conservation, our plates tell the story of their origins. By prioritizing ethical foods, we can reduce chronic diseases, protect biodiversity, and strengthen sustainable farming practices.
Instead of settling for foods that merely satisfy hunger, why not opt for choices that align with both health and conscience? Ethical nutrition lets us nurture ourselves and the world around us.
2- Pillars of Ethical and Nutritious Eating
2.1 Prioritize Local and Seasonal Foods
Choosing local and seasonal foods reduces your carbon footprint while delivering fresher, more nutrient-dense options. Seasonal produce avoids the long transportation times and emissions associated with imported foods. Plus, these foods often taste better, having ripened naturally under optimal conditions.
Studies show that eating seasonal vegetables can cut your carbon emissions by 30% compared to imported alternatives. Supporting local farmers through direct purchases or farmers’ markets creates a deeper connection with the food you eat.
2.2 Minimize Processed Foods for Maximum Benefits
Whole, minimally processed foods—like fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts—are rich in essential nutrients. Unlike processed foods, which lose nutritional value through industrial treatment and contain harmful additives, whole foods fuel your body with vitamins, fiber, and antioxidants.
A diet centered on whole, unprocessed foods reduces cardiovascular disease risk by up to 30%. Not only do these foods support energy and vitality, but they also enhance longevity and overall well-being.
2.3 Support Sustainable Farming Practices
Sustainable agricultural methods, including organic and regenerative farming, prioritize soil health and biodiversity. These practices avoid harmful chemicals, encourage ecological balance, and yield nutrient-rich crops.
By choosing organic produce, you contribute to combating soil erosion and preserving ecosystems. Ethical nutrition isn’t just about individual health—it’s about supporting systems that sustain life on Earth.
3- Incorporating Ethical Nutrition Into Everyday Life
3.1 Embrace Plant-Based Proteins
Plant-based proteins like lentils, chickpeas, and quinoa provide an eco-friendly and healthful alternative to animal products. Compared to meat, these options require fewer resources and emit significantly fewer greenhouse gases.
Studies reveal that reducing red meat consumption lowers the risk of chronic diseases by up to 15%. Moreover, plant-based proteins offer versatile flavors and textures to enjoy every day.
3.2 Combat Food Waste
Food waste is a major ethical and environmental issue. Approximately one-third of all food produced globally is wasted. Simple actions like meal planning, preserving leftovers, and using “imperfect” produce can reduce waste.
Creative solutions like composting, cooking with scraps, or using food-sharing apps help repurpose excess food. Every effort to reduce waste strengthens the ethical foundation of your diet.
3.3 Choose Ethical Labels and Certifications
Certifications such as organic, fair trade, and biodynamic provide clarity on sustainable farming and ethical practices. These labels ensure environmentally friendly production methods, fair wages for farmers, and high-quality food.
For example, choosing fair trade coffee supports small-scale producers while organic fruits avoid synthetic pesticides, protecting both your health and the planet.
4- Ethical Nutrition: Balancing Health and Enjoyment
Ethical nutrition doesn’t mean sacrificing flavor or convenience. Fresh, unprocessed foods awaken the senses and offer a richer culinary experience. From juicy fruits to crunchy vegetables, the natural world delivers abundant variety.
Knowing your choices contribute to a healthier planet amplifies the satisfaction of every meal. Ethical eating transforms food into a source of nourishment for body, mind, and environment.
5- Ethical and Nutritious Recipes to Inspire You
- Quinoa Salad with Chickpeas and Crunchy Vegetables: A protein-packed meal with fiber and vibrant flavors.
- Butternut Squash and Carrot Soup with Coconut Milk: Warm, creamy, and full of antioxidants.
- Green Smoothie with Spirulina and Spinach: An energizing blend of superfoods that boosts immunity.
Fresh Fruit Bowl with Chia Seeds: A naturally sweet and nutrient-dense dessert or breakfast option.
Conclusion
Embracing ethical nutrition means choosing health and sustainability together. From supporting local farmers to reducing food waste, every small step contributes to a brighter future. By savoring foods that respect your body and the Earth, you create a lifestyle that prioritizes well-being and environmental harmony.
So, what are you waiting for? Let your meals reflect your values and make every bite count!
Sources :
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), on global food waste issues.
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, on the benefits of unprocessed foods.
- Environmental Working Group (EWG), on the environmental impact of animal versus plant-based proteins.
- World Health Organization (WHO), on the relationship between diet and cardiovascular health.
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), on the ecological impact of local and seasonal eating.