A Guide to Emotional Balance
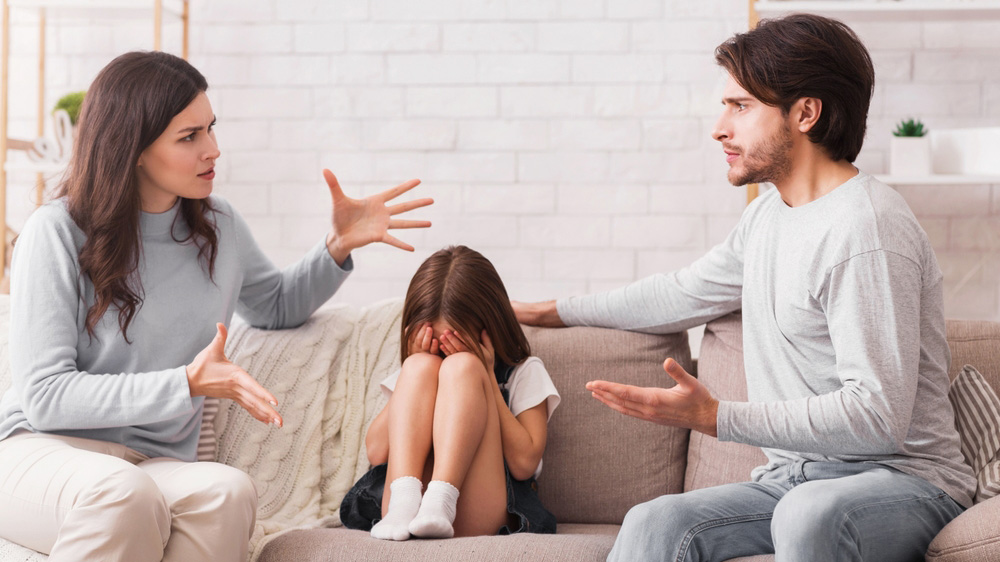
Parent-child relationships are woven with love, closeness, and a wide range of intense emotions. Between anger, frustration, joy, and tenderness, maintaining emotional balance within the family can be challenging. Knowing how to manage both your own emotions and those of your child is a crucial skill for fostering a harmonious and secure environment. How can you manage Emotions in Parent-Child Relationships? Follow this guide!
1- Understanding Emotions: A Key to Connection
Emotions are at the heart of our human experience. They inform us about our needs, boundaries, and relationships with others. In children, emotions are often expressed in raw form due to their limited vocabulary and maturity to verbalize them properly.
2- The Role of Emotions in Children
Children feel everything intensely: anger erupts, sadness overwhelms, and joy radiates. These emotions are neither good nor bad—they are signals to be understood. When a child has a tantrum or bursts into tears, they are expressing a need or a lack of understanding about the world around them.
3- The Role of Emotions in Parents
Parents also experience emotional storms—impatience, fear, guilt… Their own emotional regulation directly influences their child’s. A parent who reacts with anger to their child’s outburst may unintentionally escalate the situation.
4- Welcoming and Validating Emotions
Rather than suppressing or minimizing a child’s emotions (“It’s nothing, stop crying!”), it is better to acknowledge them with kindness. Telling a child that their emotions are valid helps them understand and manage their feelings.
5- Techniques for Emotion Validation
- Name the emotion: “I see that you are angry because your toy is broken.”
- Validate their feelings: “It’s normal to feel sad when you lose something important.”
- Use empathy: “I understand that you’re frustrated—I feel that way sometimes too.”
A child who feels heard and understood gradually learns to regulate their emotions better.
6- The Importance of Emotional Regulation
Emotional regulation helps a child learn to manage their emotions rather than being overwhelmed by them. It involves several key steps:
1. Recognizing the Emotion
Encouraging a child to identify what they are feeling is essential. Using an emotion chart or illustrated stories can help them put words to their emotions.
2. Breathing and Calming Down
Deep breathing, coloring, or having a quiet space can be effective tools to soothe an emotional storm.
3. Finding an Appropriate Solution
Once the emotion has been calmed, help the child find solutions to their problem. For example: “How could you ask for that toy without shouting?”
7- The Parent’s Role as a Model
Children learn primarily through imitation. A parent who expresses their emotions calmly and uses healthy coping strategies sets a positive example for their child.
How to Be a Role Model
- Express emotions without aggression: “I feel frustrated because I lost my keys. I’m going to take a deep breath.”
- Demonstrate regulation strategies: “I’m going to take a short walk to calm down.”
- Apologize when necessary: “I got upset too quickly—I’m sorry.”
8- Creating an Emotionally Safe Family Environment
A child who feels emotionally secure is better equipped to manage their emotions. Key principles include:
✅ Setting clear and kind boundaries: A stable framework reassures the child.
✅ Encouraging emotional autonomy: Allowing the child to find their own solutions.
✅ Prioritizing quality time: Play, conversations, and rituals strengthen the parent-child bond.
Conclusion
Managing emotions in parent-child relationships requires time, patience, and a great deal of empathy. By guiding your child with kindness, teaching them to understand and regulate their emotions, you offer them an invaluable gift: the ability to grow with confidence in themselves and in their relationships with others.
Sources :
- American Psychological Association – Emotional Regulation in Children
- Harvard University – Parenting and Emotional Development
- Child Mind Institute – Helping Kids Manage Emotions
- Psychology Today – The Science of Emotions
- National Institute of Mental Health – Children’s Emotional Health