Regaining Control Over Your Emotions in Daily Life
In our fast-paced society, where stress and constant demands overwhelm us, it is easy to fall into emotional overconsumption. This phenomenon, which affects everyone to varying degrees, results in an excessive accumulation of emotions, often poorly managed, that ultimately impact our overall well-being, particularly our relationship with food.
What if we learned to process our emotions rather than mindlessly consuming them? Let’s explore how to regulate this emotional overload and restore balance between our mind and body.
1- What Is Emotional Overconsumption?
Emotional overconsumption is the tendency to absorb an overload of emotions without properly processing them. It can manifest in several ways:
- Hyper-emotional connectivity: Being overly affected by others’ emotions, absorbing external influences too easily.
- Compulsive need for stimulation: Constantly seeking strong sensations (TV shows, movies, social media, heated discussions) to avoid emotional emptiness.
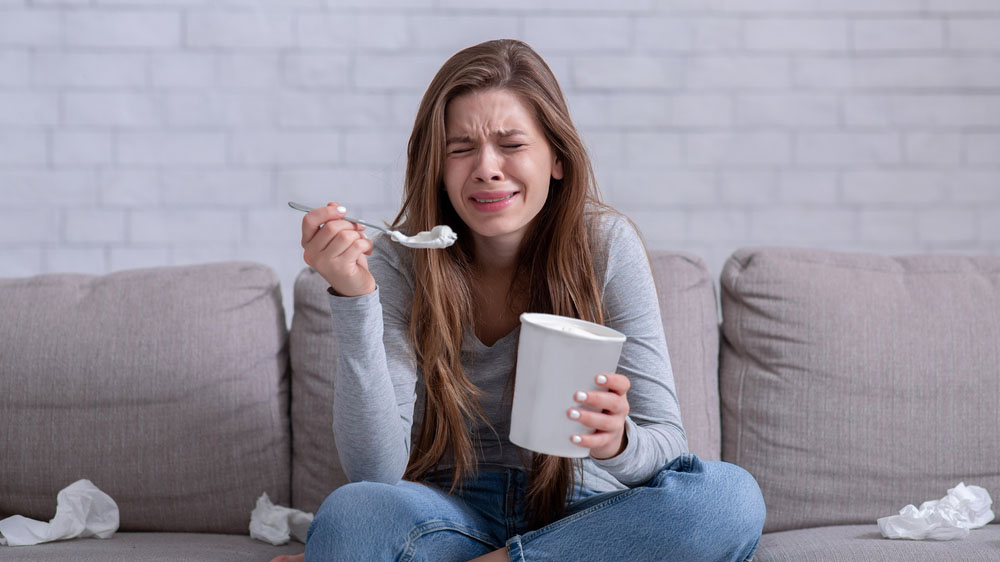
- Emotional eating: Using food to fill an emotional void, manage stress, or escape uncomfortable feelings.
This phenomenon is exacerbated by modern life, where everything is instant, and we are constantly exposed to intense emotional stimuli. The result? A real case of emotional indigestion that weighs heavily on our well-being.
2- The Connection Between Emotions and Eating: A Matter of Digestion
Our emotions directly influence our relationship with food. Who hasn’t reached for a chocolate bar after a tough day? Who hasn’t craved sugar after an argument or bad news?
This is due to the role of dopamine and cortisol, two hormones that influence our eating behaviors in response to emotions:
- Cortisol, the stress hormone, encourages the body to store fat and seek out sugary, fatty foods to “cope” with perceived difficulties.
- Dopamine, the pleasure hormone, is released when we eat comforting foods, reinforcing the connection between emotions and eating.
When we allow ourselves to be carried away by emotional overconsumption, we risk developing compulsive eating behaviors, leading to weight gain, poor digestion, and an unhealthy relationship with food.
So how can we regain a balanced diet and a peaceful relationship with our emotions?
3- Techniques to Avoid Emotional Overconsumption
1. Identify Your Emotional Triggers
The first step in regaining control is understanding what triggers emotional excess. Is it work stress? Boredom? A breakup?
➡ Practical Exercise: Keep an emotional journal. Write down what you feel before eating and identify the emotions that drive you to consume certain foods.
2. Learn to Recognize True Hunger
Emotional hunger is sudden, urgent, and often focused on comfort foods, while physical hunger develops gradually and can be satisfied with healthy foods.
➡ Tip: When you feel a sudden urge to eat, take a few minutes to ask yourself: “Am I really hungry, or is this an emotion driving me to eat?”
3. Practice Mindful Eating
Mindful eating helps rebuild a healthy relationship with food by allowing you to savor each bite.
➡ Simple Exercise: During your next meal, put down your utensils between bites, take time to taste the flavors, and listen to your body’s satiety signals.
4. Find Healthy Alternatives to Manage Emotions
If we tend to use food as emotional compensation, why not replace these habits with healthier behaviors?
➡ Ideas to Try:
- Go outside for fresh air or take a short walk.
- Practice deep breathing or a quick meditation session.
- Call a loved one to chat instead of turning to the fridge.
5. Create a Soothing Emotional Environment
Our environment greatly influences how we handle emotions. A stressful or chaotic setting can increase the urge to use food as a coping mechanism.
➡ Steps to Implement:
- Declutter your living space to promote a calm atmosphere.
- Limit exposure to social media and stressful news.
- Establish well-being rituals like a relaxing bath, reading, or listening to soft music.
6. Balance Your Meals to Prevent Emotional Cravings
A well-balanced diet helps regulate stress and satiety hormones.
➡ Prioritize:
- Proteins and fiber to avoid blood sugar spikes that trigger cravings.
- Magnesium-rich foods (dark chocolate, almonds, bananas) to regulate stress.
- Omega-3s (fatty fish, flaxseeds) to support brain function and emotional balance.
Conclusion : Embracing Emotions Instead of Escaping Them
Avoiding emotional overconsumption doesn’t mean suppressing emotions but rather welcoming them with kindness.
It is essential to:
✔ Allow yourself to feel without immediately trying to fill the void with distractions or food.
✔ Express emotions constructively (writing, art, conversation).
✔ Accept that emotional discomfort is part of life and that it is temporary.
By adopting a more conscious and compassionate approach, we can restore a peaceful relationship with both our emotions and our eating habits, ensuring lasting well-being in daily life.
Sources :
- Harvard Health Publishing – Emotional eating: Why it happens and how to stop it
- Psychology Today – The connection between emotions and eating
- National Institute of Mental Health – Understanding stress and eating behaviors
- Medical News Today – How emotions impact eating habits
- Mayo Clinic – Mindful eating: How to manage emotional eating