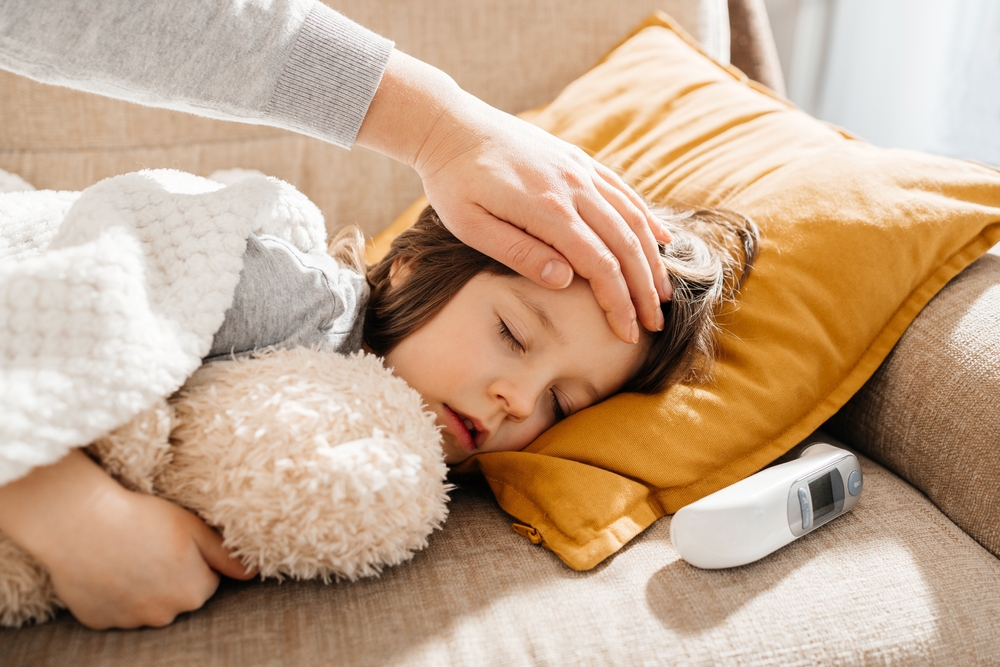
Sleep isn’t just about resting—it’s about taking care of your body and mind. But did you know that quality sleep can actually protect you from numerous diseases? Often underestimated, sleep plays a crucial role in preventing cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and metabolic diseases. Ready to dive into the world of sleep and discover how it can optimize your health? Follow this guide to understand why a good night’s sleep is not a luxury, but a true health ally!, let ‘s discover the relationship between sleep and physical health.
1. Sleep: The Overlooked Pillar of Health
Sleep isn’t wasted time—quite the opposite! While you dream, your body works hard. Nighttime is key for cellular repair, hormonal balance, and memory consolidation. Experts recommend that adults sleep between 7 and 9 hours per night, yet one in three French adults is sleep-deprived—a problem with serious health consequences, so your sleep and physical health must be considered together.
The benefits of sleep extend across nearly every part of our body. Quality sleep boosts immunity, regulates blood sugar levels, and stabilizes mood. On the other hand, chronic sleep deprivation can lead to serious disorders such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and neurological issues.
2. The Link Between Sleep and Cardiovascular Diseases
Short nights don’t just drain your energy—they strain your heart. A study published by Santé Publique France found that sleep deprivation increases the risk of cardiovascular issues, including heart attacks and strokes. During sleep, blood pressure naturally drops, giving the cardiovascular system time to recover. When sleep is too short or disrupted, blood pressure remains high, increasing the risk of serious conditions.
3. Immunity and Sleep: A Winning Team
Want to avoid frequent colds? Take care of your sleep! Sleep plays a vital role in producing cytokines, molecules essential for fighting infections and inflammation. A study from the University of Paris revealed that people who sleep fewer than six hours per night have a significantly higher risk of respiratory infections.
4. Sleep as a Shield Against Metabolic Diseases
The link between sleep and metabolism is surprising. Too little sleep disrupts hunger-regulating hormones, such as leptin and ghrelin. This explains why sleep-deprived individuals are more prone to snacking and weight gain. Over time, this imbalance contributes to obesity and type 2 diabetes.
5. A Healthy Brain Thanks to Sleep
Sleep doesn’t just restore the body—it also cleanses the brain. During sleep, the brain eliminates toxins accumulated throughout the day, reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. Research shows that sleep disturbances are one of the earliest symptoms observed in Alzheimer’s patients.
6. Tips for Better Sleep
Don’t worry—you can improve your sleep quality! Here are some simple tips to maximize your nights:
✔ Stick to a routine: Go to bed and wake up at the same time each day.
✔ Avoid screens before bed: Blue light disrupts melatonin production, the sleep hormone.
✔ Create a sleep-friendly environment: A dark, quiet, and cool room improves sleep quality.
✔ Watch your diet: Avoid caffeine and alcohol in the evening, and opt for a relaxing herbal tea instead.
Conclusion
Sleep is a silent superhero. Every well-rested night is a step toward better health. So, the next time you’re tempted to binge-watch your favorite series instead of getting an extra hour of sleep, remember: sleeping well is an investment in your future., sleep and physical health are ultimately linked.
Sources:
- National Sleep Foundation – « How Sleep Affects Physical Health »
- Harvard Medical School – « Sleep and Your Health »
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – « Sleep and Chronic Disease »
- Mayo Clinic – « Sleep Disorders: An Overview »
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine – « Sleep as a Vital Sign »